Portfolio returns: Q3 2025
| Total Return | 1M | 3M | YTD | 1YR | 3YR | 5YR | 10YR | Since Inc. (Jan 30, 2023) |
IG Target Education 2030 Portfolio F | 3.19
| 5.80
| 9.08
| 12.05
| 11.82
| |||
Quartile rankings | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total Return | 1M | 3M | YTD | 1YR | 3YR | 5YR | 10YR | Since Inc. (Jan 30, 2023) |
IG Target Education 2030 Portfolio F | 3.19
| 5.80
| 9.08
| 12.05
| 11.82
| |||
Quartile rankings | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
 The IG Target Education 2030 Portfolio underperformed its benchmark over the quarter. Country positioning in equities was additive; asset allocation and sector selection in U.S. equities were flat, while manager selection faced headwinds.
The IG Target Education 2030 Portfolio underperformed its benchmark over the quarter. Country positioning in equities was additive; asset allocation and sector selection in U.S. equities were flat, while manager selection faced headwinds.
Asset allocation positioning was flat over the quarter. While an overweight position in Japanese and EAFE equities contributed to the performance, it was offset by an underweight to U.S. equities and an underweight to fixed income. Country relative value positioning was a main contributor over the quarter, driven by overweight positions to Japan and China. Underweights were fairly flat over the quarter. An overweight in financials, energy and health care contributed collectively, while an underweight to utilities and industrials detracted.
Active equity managers were challenged over the quarter, driven by the underperformance in T. Rowe U.S. equity, Makenzie Canadian equity and Fidelity Canadian equity funds.
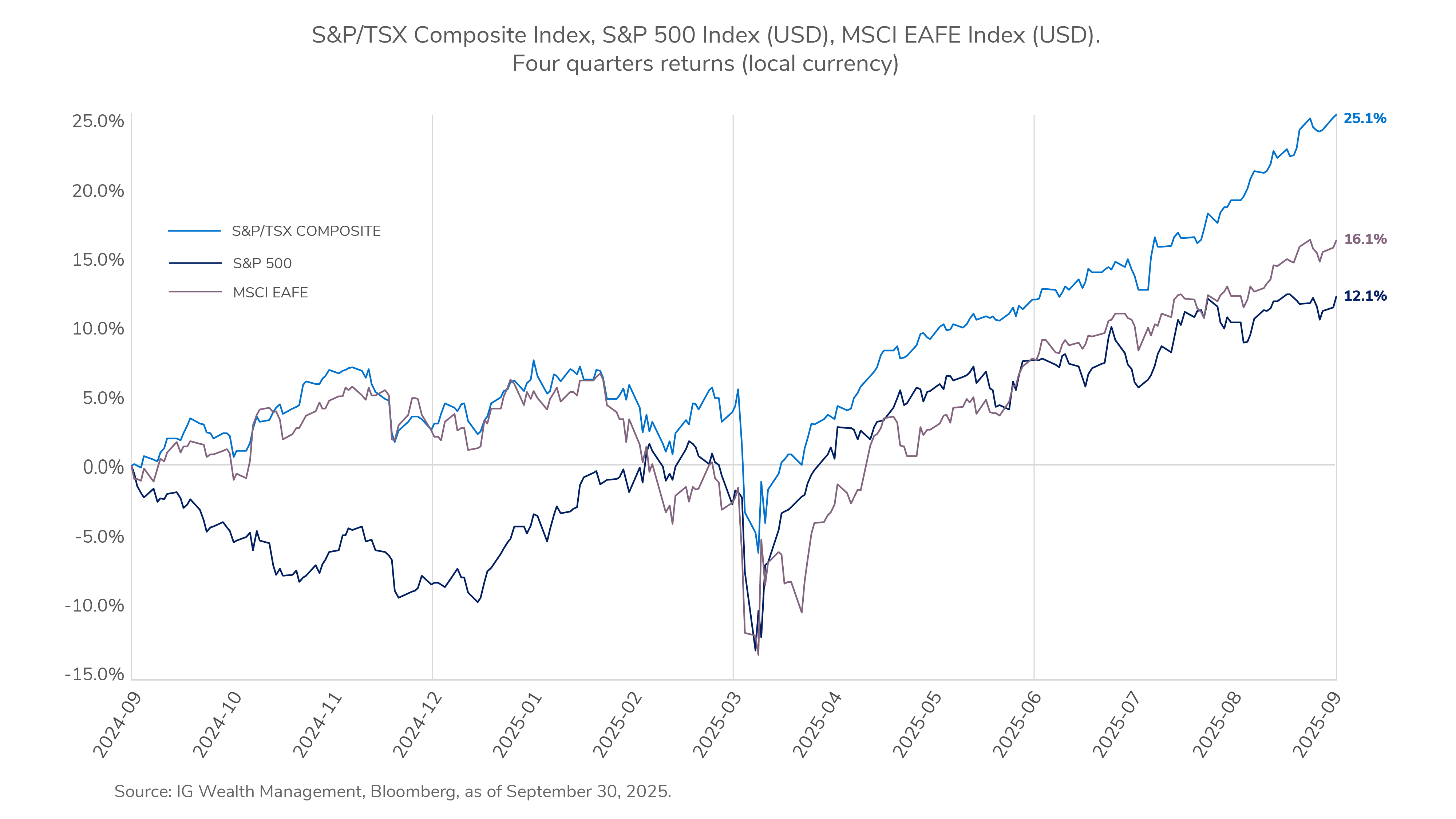
The third quarter delivered broad gains across asset classes, with market performance largely overriding a backdrop of cautious sentiment. Investors looked past persistent trade policy headlines, increasingly treating the U.S. administration's tariff policy as noise rather than a core risk. The primary catalysts for the positive performance were a subtle shift toward lower-interest-rate expectations and resilient corporate earnings.
Signals from the U.S. Federal Reserve of imminent rate cuts were followed by a quarter percentage cut in September. Government bond yields eased into the quarter's end, supporting bond prices, while corporate bonds outperformed government bonds.
While European cohesion may be a theme in markets, U.S. economic policy has clearly exhibited some recent fiscal-monetary fissures. Our portfolios remain positioned for a scenario in which the U.S. Federal Reserve (the Fed) pursues a cycle of rate cuts despite persistent firmness in inflation and structural tightness in labour markets. The Fed’s September meeting captured these tensions as the central bank simultaneously initiated an easing cycle while upgrading both its growth and inflation forecasts. A policy outturn along these lines would mark a clear departure from historical patterns.
While consensus narratives may consider this move toward a rate-cutting position as a mix of malfeasance and malpractice, we believe this is misplaced. Rather, the two structural forces of debt sustainability (ensuring interest rates remain below economic growth rates) and the onshoring of critical industries likely necessitate the policy outturns that we are currently observing. We increased our fixed income underweight in both the U.S. and Europe earlier in September, as bond yields fell following a weak U.S. employment report. We believe this price action reflected investors mistaking a structural slowdown in U.S. job gains for cyclical weakness.
Commissions, fees and expenses may be associated with mutual fund investments. Read the prospectus and speak to an IG Advisor before investing. The rate of return is the historical annual compounded total return as of September 30, 2025, including changes in value and reinvestment of all dividends or distributions. It does not take into account sales, redemption, distribution, optional charges or income taxes payable by any securityholder that would have reduced returns. Mutual funds are not guaranteed, values change frequently and past performance may not be repeated. Mutual funds and investment products and services are offered through the Mutual Fund Division of IG Wealth Management Inc. (in Quebec, a firm in financial planning). And additional investment products and brokerage services are offered through the Investment Dealer, IG Wealth Management Inc. (in Quebec, a firm in financial planning), a member of the Canadian Investor Protection Fund.
This commentary may contain forward-looking information which reflects our or third-party current expectations or forecasts of future events. Forward-looking information is inherently subject to, among other things, risks, uncertainties and assumptions that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed herein. These risks, uncertainties and assumptions include, without limitation, general economic, political and market factors, interest and foreign exchange rates, the volatility of equity and capital markets, business competition, technological change, changes in government regulations, changes in tax laws, unexpected judicial or regulatory proceedings and catastrophic events. Please consider these and other factors carefully and do not place undue reliance on forward-looking information. The forward-looking information contained herein is current only as of September 30, 2025. There should be no expectation that such information will in all circumstances be updated, supplemented or revised whether as a result of new information, changing circumstances, future events or otherwise.
This commentary is published by IG Wealth Management. It represents the views of our Portfolio Managers and is provided as a general source of information. It is not intended to provide investment advice or as an endorsement of any investment. Some of the securities mentioned may be owned by IG Wealth Management or its mutual funds, or by portfolios managed by our external advisors. Every effort has been made to ensure that the material contained in the commentary is accurate at the time of publication, however, IG Wealth Management cannot guarantee the accuracy or the completeness of such material and accepts no responsibility for any loss arising from any use of or reliance on the information contained herein.
Trademarks, including IG Wealth Management and IG Private Wealth Management, are owned by IGM Financial Inc. and licensed to subsidiary corporations.
©2025 IGWM Inc.